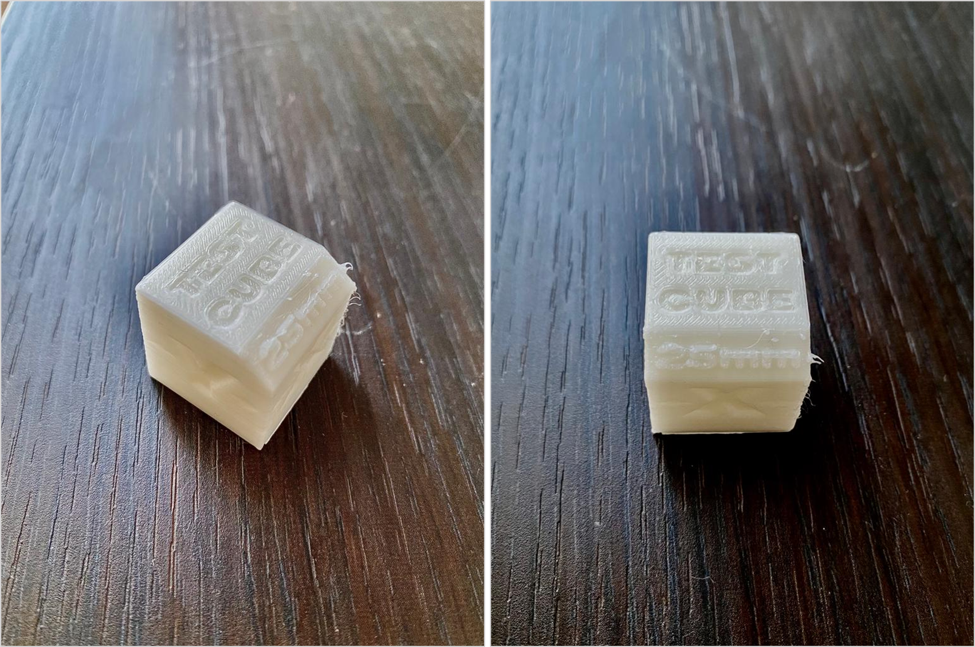
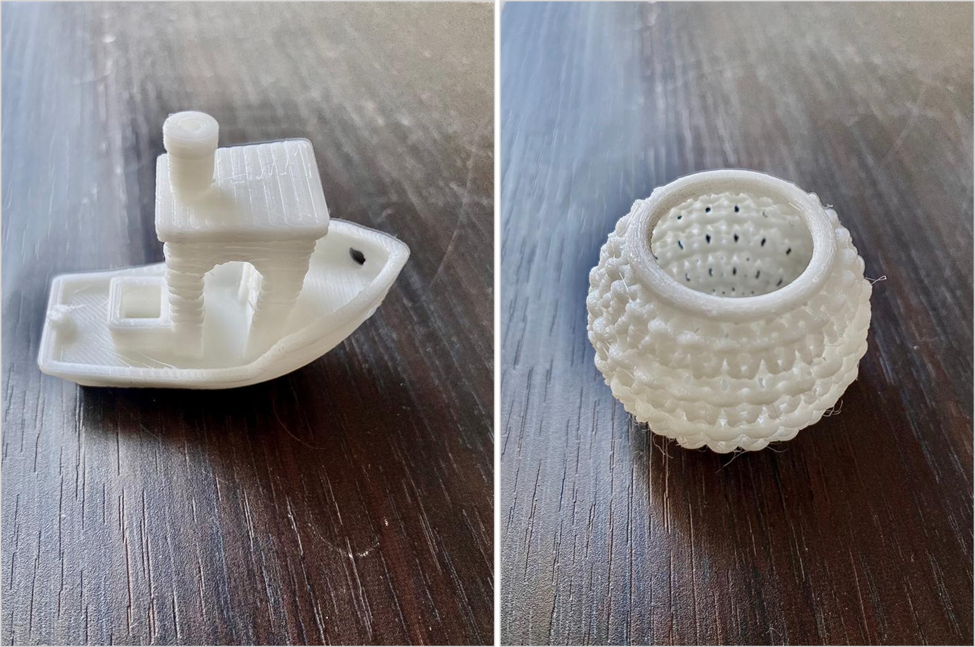
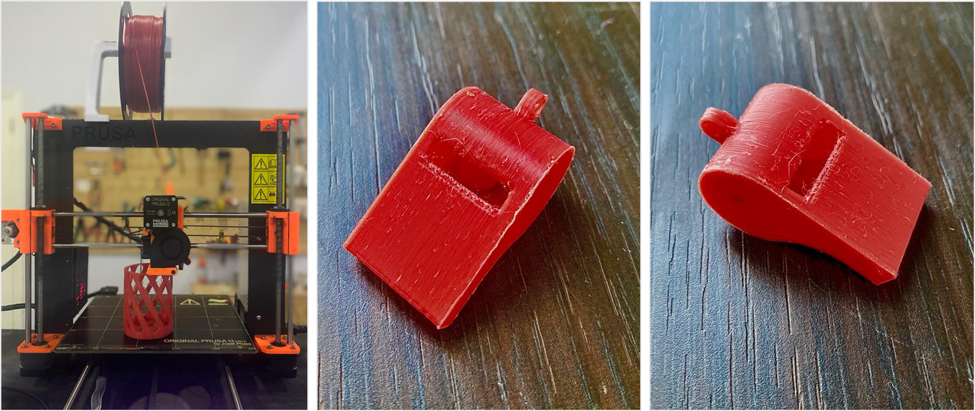
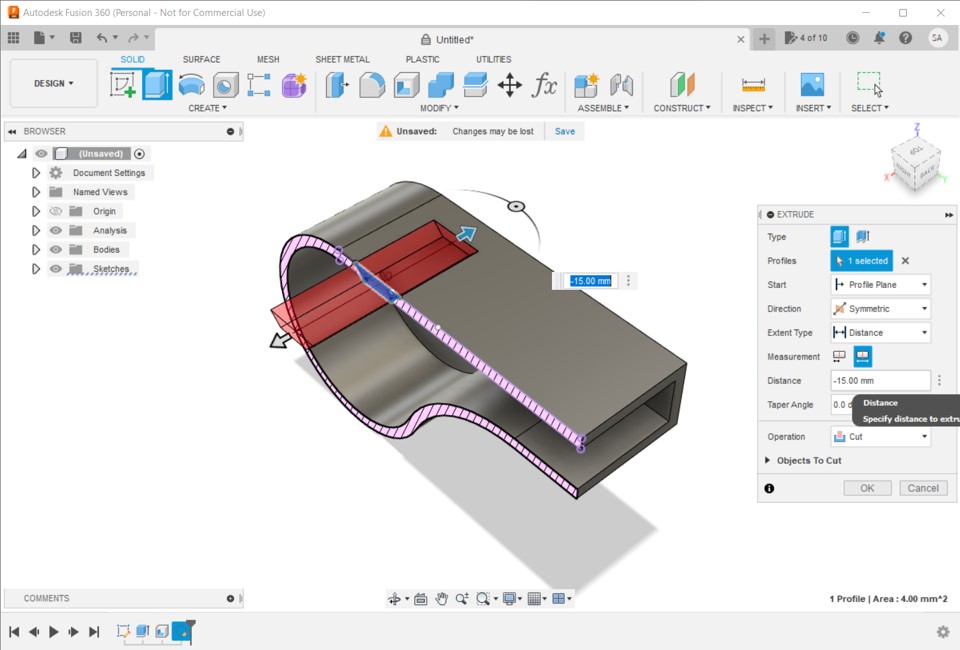
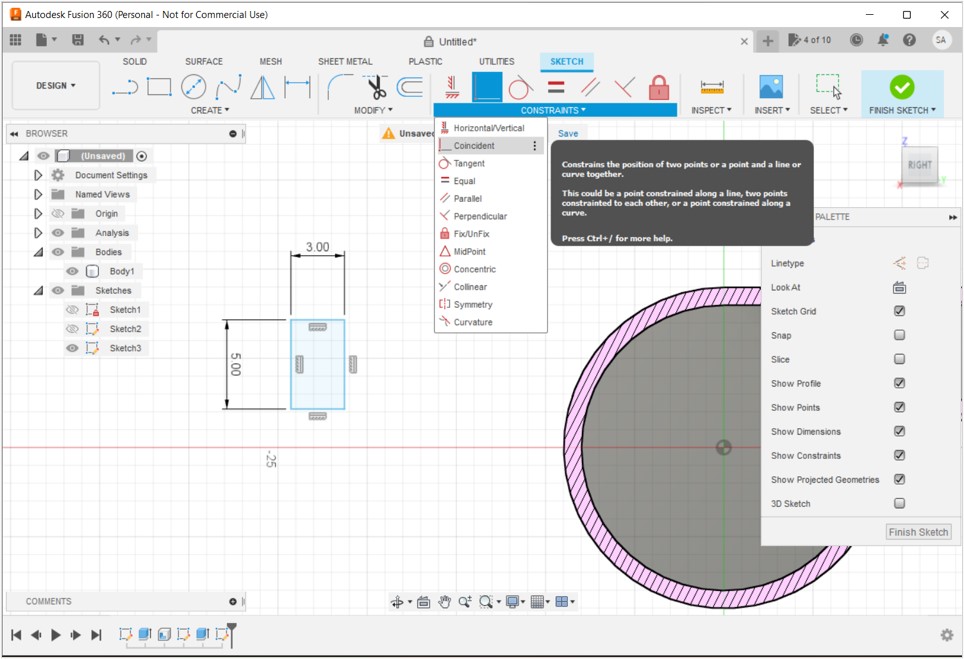
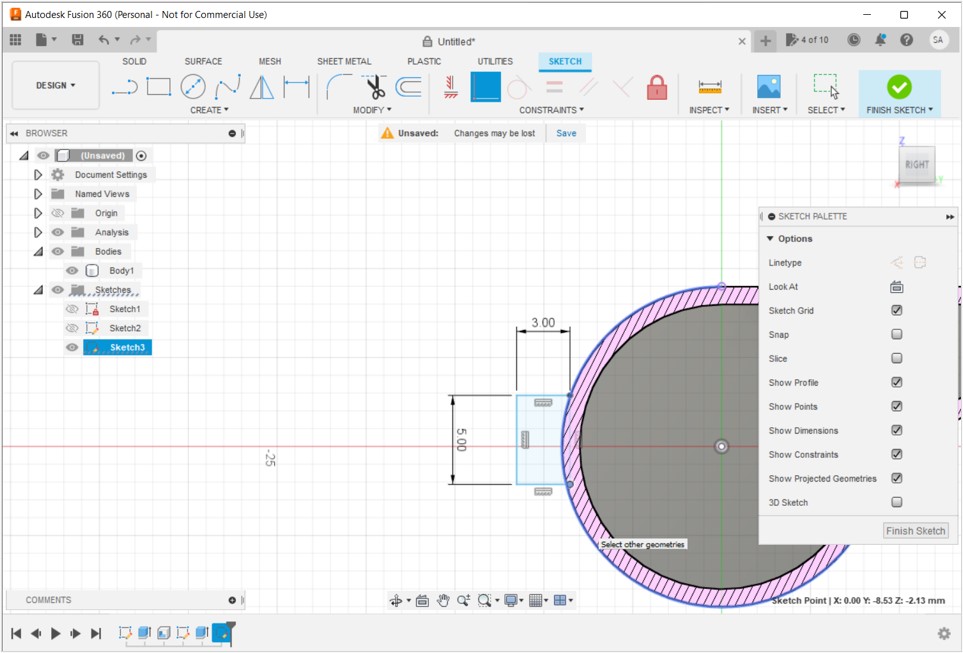
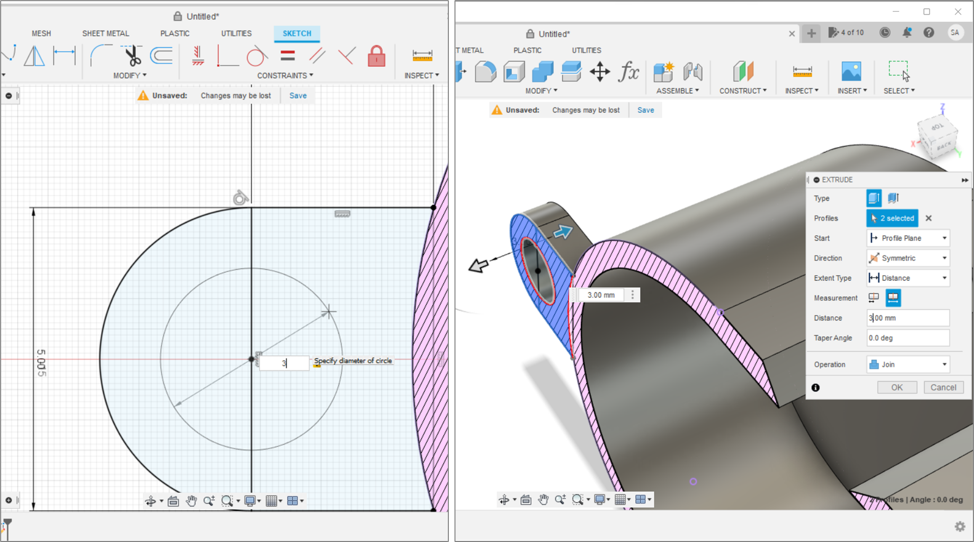
3D PRINTING AND SCANNING
This week we were introduced to different 3D machines, where we experimented with them in groups and individually. First of all, we learned all about the machines before using them:
What is 3D Printing?
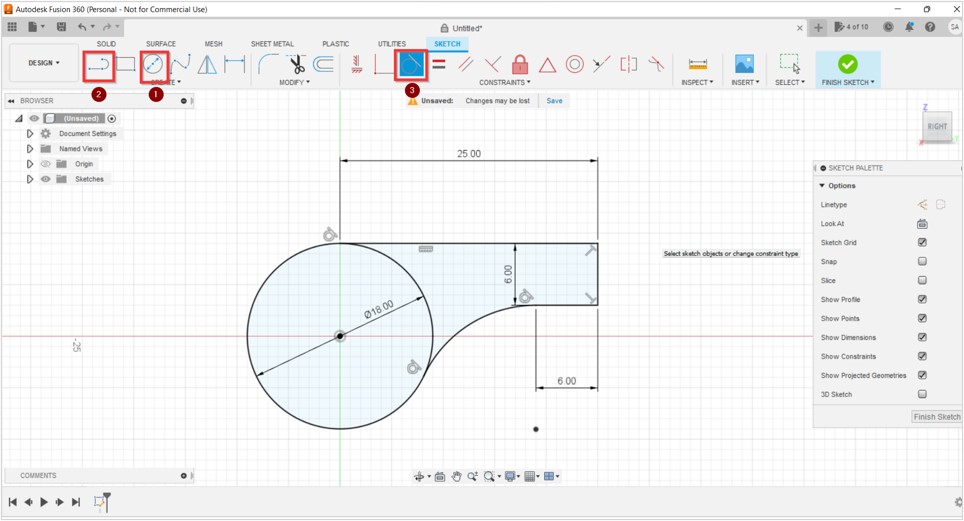
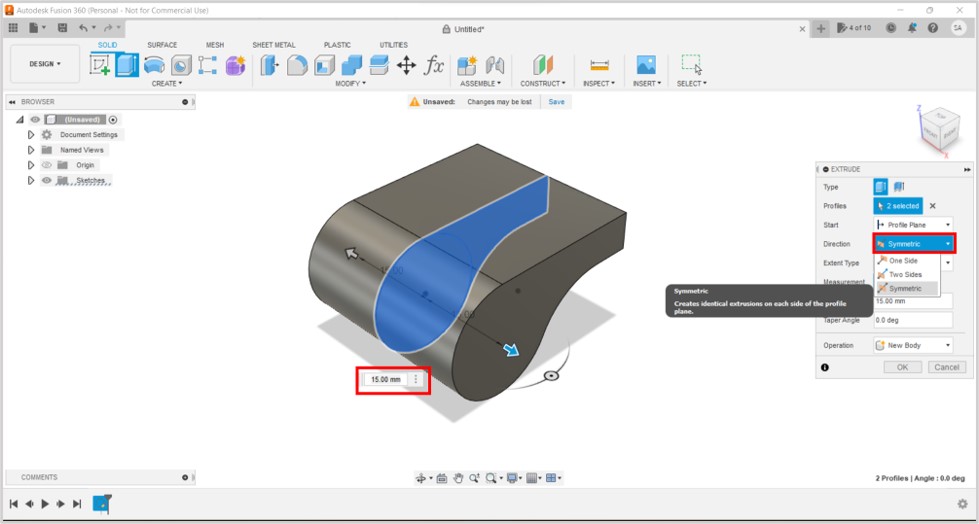
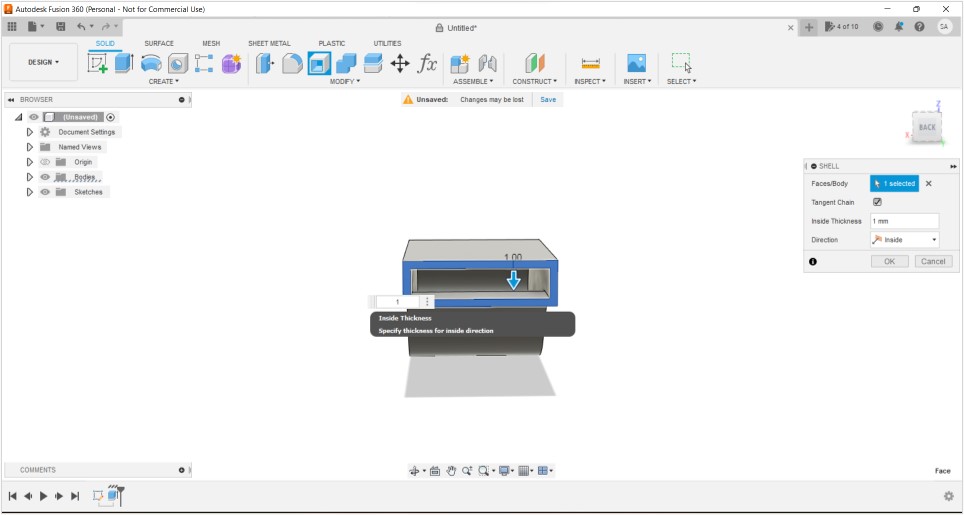
3D printing uses computer-aided design to create three-dimensional objects through a layering method. Sometimes referred to as additive manufacturing, 3D printing involves layering materials, like plastics, composites or bio-materials to create objects that range in shape, size, rigidity and color.
Types of 3D Printers:
The three most established types of 3D printers for plastics parts are stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and fused deposition modeling (FDM). The table down below illustrates the differences between these printers, in terms of filaments (materials) they can take, the accuracy, etc.
| Types | How it works | Materials | Strenghts | Common applications | DIM-accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | It works by pushing a plastic filament through a heated nozzle. The molten plastic is then placed down layer by layer until the part is complete. | ABS, PLA, ETG, Etc. | Cheap, Easy to operate | Prototyping, Hobbyist parts, Manufacturing Jigs | 0.5 mm |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | It works by curing a liquid photopolymer into the final part by tracing a high-powered laser in the shape of the part cross-section onto the build plate. This process continues while each subsequent layer is polymerized onto the previous one. | Polycarbonate-Like, ABS-Like, Polypropylene like | High detail | Casting patterns, Prototypes | 0.1 mm |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | It works by placing down a layer of powdered plastic and tracing out the cross-section of the part with a laser. This laser melts the powder and fuses it. Another layer of plastic powder is laid over the previous one and the laser melts the cross-section shape while also fusing it into the previous layer. | Polyamide 12, Glass Filled Nylon | Isotropic materials, No support structures needed | Flame retardant components, Medical devises | 0.3 mm |
Types of 3D printer filaments:
The most common filament types are acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polylactic acid (PLA). Most basic 3D printers are designed to exclusively use these filaments. In this assignment we used PLA. Down below is a table of PLA filament properties.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | 126 °F (52 °C) |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 50 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 80 MPa |
| Impact Strength (Unnotched) IZOD (J/m) | 96.1 |
| Shrink Rate | 0.37-0.41% (0.0037-0.0041 in/in) |
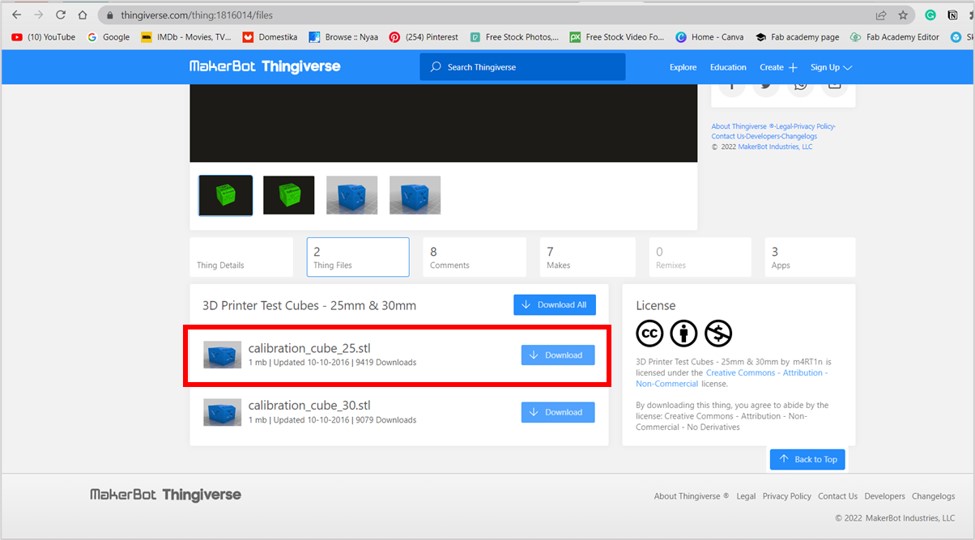
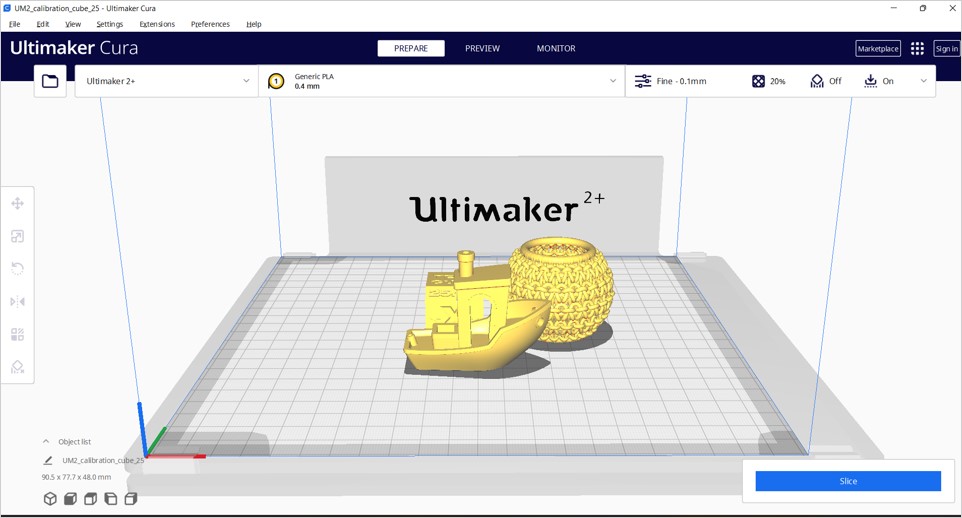
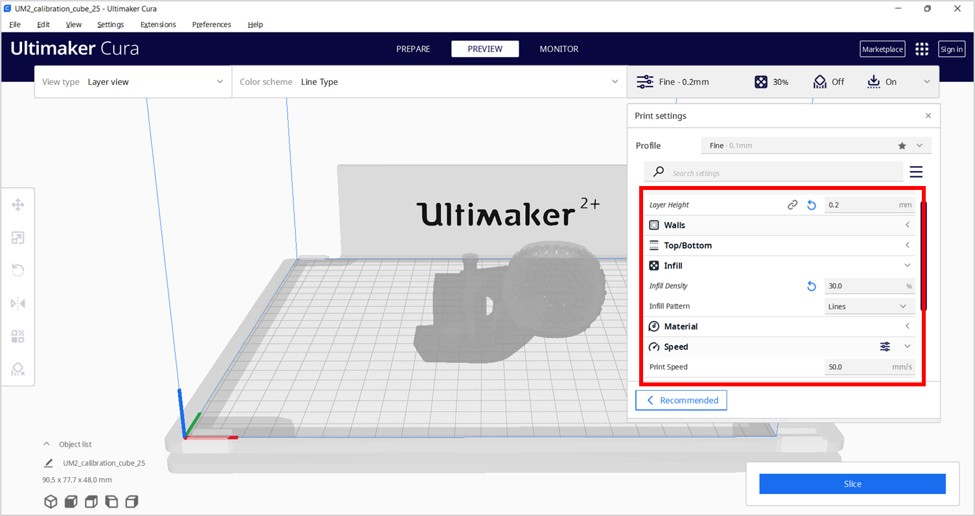
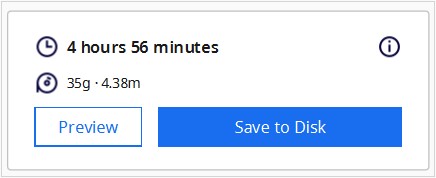
Scroll down to learn about how we used the printers.